
Control Systems
Optimizing Processes with Precision Control and Automation
A Control System is a set of interconnected components designed to manage, command, or regulate the behavior of other systems or devices to achieve desired outputs. By controlling variables in real-time, a control system ensures that a process stays within the set parameters, achieving the desired results effectively and efficiently
Input
The desired value or setpoint that the system aims to achieve (e.g., desired temperature or motor speed)

- 1.456

- 4.9
- 1.456
Controller
The brain of the system, it processes the input and feedback to generate a control signal (e.g., PID controller), which is sent to the actuator
Actuator
Converts the control signal into a physical action, like adjusting the position of a valve or motor speed

- 1.456

- 4.9
- 1.456
Plant/Process
The actual system being controlled, such as the temperature of a room or the speed of a motor.
Feedback (Sensor/
Measurement)
Measures the system’s output and sends it back to the controller to ensure the output matches the setpoint.

- 1.456

- 4.9
- 1.456
Output (Controlled Variable)
The actual result of the system, reflecting the controlled variable such as the temperature, speed, or pressure.
Types of Control Systems
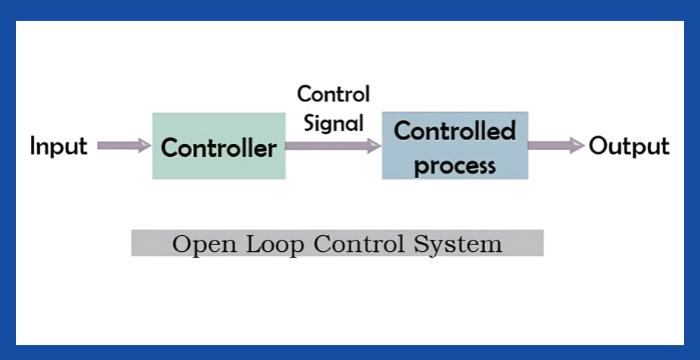
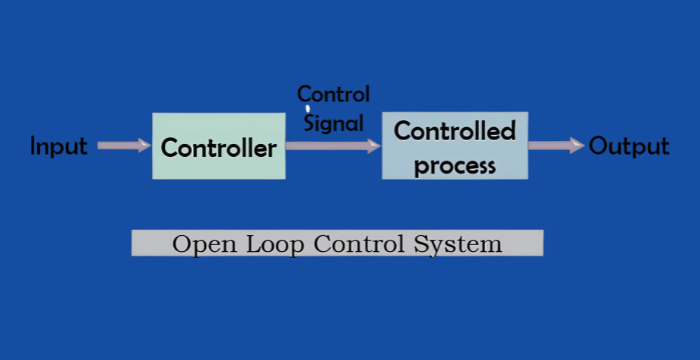
Open-Loop Control System
No feedback; output has no effect on control action.

Closed-Loop (Feedback) Control System
Uses feedback to adjust the input for the desired output.
Automatic vs. Manual Control
No human intervention (e.g., cruise control in cars).
Applications of Control Systems
Control systems play a vital role in multiple industries by ensuring the precision and efficiency of dynamic processes. Here are some examples:
Industrial Automation
Robotics, CNC machines, assembly lines.
Automotive
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), Cruise Control.
Home Appliances
Flight control systems.
Environmental Monitoring
Air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines
Power Systems
Voltage regulation in electrical grids
Examples of Control Systems in Action
Temperature Control in HVAC
Regulates heating and cooling to maintain comfort levels in buildings.
Speed Control in Motors
Ensures that motor speed remains constant for machines in factories
Position Control in Robotics
Directs robotic arms and other machinery for precise movements
Why Control Systems Matter
Control systems are essential for stability, accuracy, and efficiency in dynamic processes. Without control systems, complex operations such as manufacturing, energy production, and even household appliances would be inefficient and prone to failure.
Contact Us
Take Control of Your Operations Today
We will reply within 24 hours
